Financial & managerial accounting 16th edition – Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of financial and managerial accounting with the 16th edition of this comprehensive guide. This definitive text unravels the intricacies of financial reporting, cost analysis, budgeting, and performance measurement, empowering readers with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of modern business.
Delving into the fundamental principles and evolving landscape of financial and managerial accounting, this book provides a solid foundation for understanding the critical role these disciplines play in driving informed decision-making and ensuring organizational prosperity.
1. Overview of Financial and Managerial Accounting 16th Edition

The 16th edition of Financial and Managerial Accounting provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental principles and practices of financial and managerial accounting. It covers the key concepts, theories, and techniques used by accountants to record, analyze, and interpret financial data for various stakeholders.
Brief History of Financial and Managerial Accounting
Financial accounting emerged in the 15th century with the development of double-entry bookkeeping. Managerial accounting, on the other hand, evolved in the early 20th century as businesses sought to improve their internal decision-making processes.
Role in Business Decision-Making
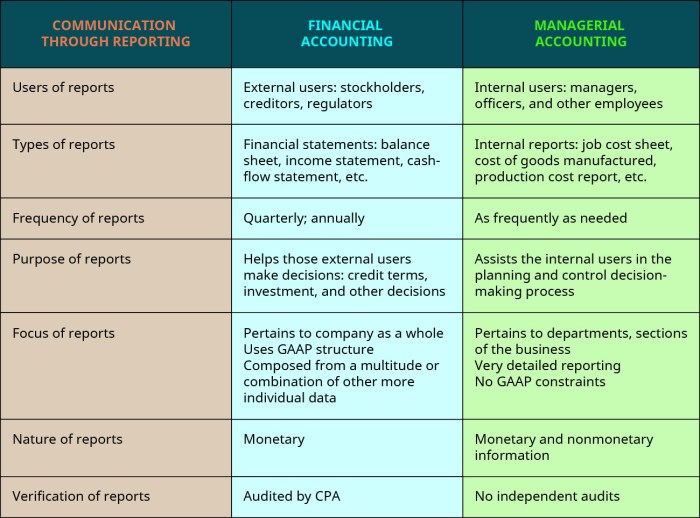
Financial and managerial accounting play crucial roles in business decision-making. Financial accounting provides external users with information about a company’s financial performance and position, while managerial accounting provides internal users with information to support planning, control, and decision-making.
2. Financial Accounting
Purpose and Objectives
Financial accounting aims to provide accurate and reliable financial information about an organization to external users, such as investors, creditors, and regulatory agencies.
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
Financial accounting is governed by accounting standards, such as GAAP and IFRS, which ensure consistency and comparability of financial statements across different companies.
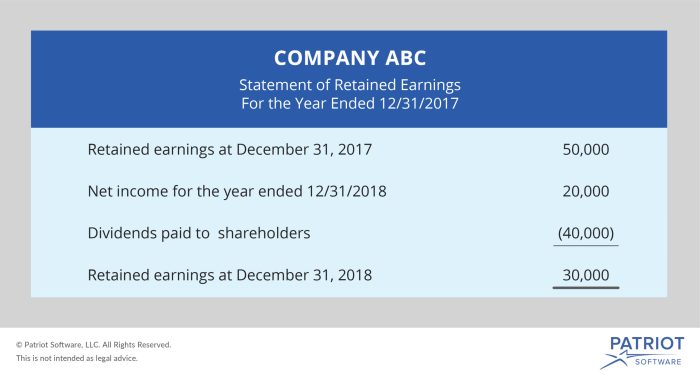
Accounting Cycle and Financial Statements
The accounting cycle involves recording, classifying, summarizing, and reporting financial transactions in financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows.
3. Managerial Accounting

Purpose and Objectives
Managerial accounting focuses on providing information to internal users, such as managers and executives, to support their decision-making processes.
Types of Managerial Accounting Reports
Managerial accounting reports include cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis, budgeting, performance evaluation, and capital budgeting.
Use of Managerial Accounting Information
Managerial accounting information is used for planning, decision-making, and control within an organization.
4. Financial Statement Analysis
Purpose and Objectives
Financial statement analysis involves evaluating a company’s financial performance and condition using financial ratios and other techniques.
Types of Financial Ratios
Financial ratios are used to measure profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency. Common ratios include gross profit margin, return on assets, and debt-to-equity ratio.
Use of Financial Statement Analysis, Financial & managerial accounting 16th edition
Financial statement analysis helps investors, creditors, and other stakeholders assess a company’s financial health and make informed investment decisions.
5. Cost Accounting

Purpose and Objectives
Cost accounting involves tracking, analyzing, and allocating costs to products, services, or departments to support decision-making and control.
Types of Costing Systems
Common costing systems include job order costing, process costing, and activity-based costing.
Use of Cost Accounting Information
Cost accounting information is used for pricing decisions, inventory valuation, and cost control.
6. Budgeting
Purpose and Objectives
Budgeting involves creating a financial plan that Artikels the expected revenues and expenses for a specific period.
Types of Budgets
Budgets can be classified as operating budgets, capital budgets, or cash budgets.
Use of Budgets
Budgets are used for planning, coordinating activities, and controlling expenses.
7. Performance Measurement
Purpose and Objectives
Performance measurement involves evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of an organization’s operations.
Types of Performance Measures
Performance measures include financial metrics, operational metrics, and customer satisfaction metrics.
Use of Performance Measurement
Performance measurement helps organizations identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions.
Essential FAQs: Financial & Managerial Accounting 16th Edition
What are the key differences between financial and managerial accounting?
Financial accounting focuses on reporting financial information to external stakeholders, while managerial accounting provides information for internal decision-making.
What are the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)?
GAAP is a set of accounting standards that govern the preparation of financial statements.
What is the purpose of financial statement analysis?
Financial statement analysis helps users evaluate a company’s financial performance and condition.
What is the role of cost accounting in decision-making?
Cost accounting provides information that helps managers make informed decisions about pricing, production, and resource allocation.
How can budgeting contribute to organizational success?
Budgeting helps organizations plan for the future, allocate resources effectively, and monitor performance.