Classify the following as intensive or extensive properties of gold: density, melting point, mass, and volume. Intensive properties are independent of the amount of substance, while extensive properties depend on the amount of substance.
Gold is a precious metal with a wide range of applications. It is used in jewelry, coinage, electronics, and dentistry. Gold is also an important investment asset.
Physical Properties of Gold

Gold exhibits a unique combination of physical properties that contribute to its distinctive characteristics and value. These properties can be classified into two categories: intensive and extensive properties.
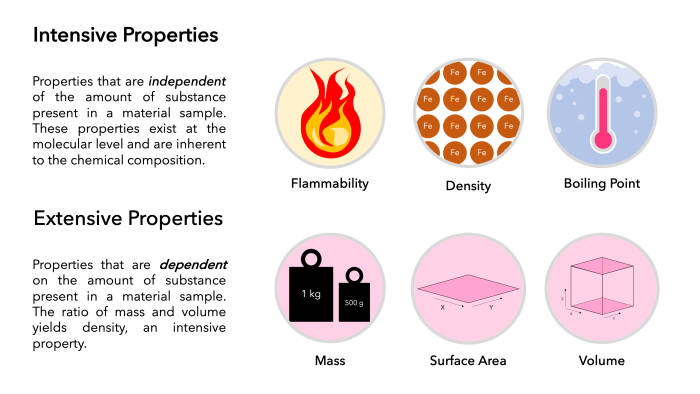
Intensive Properties
Intensive properties are those that are independent of the amount of gold present. They include:
- Density:Gold has a high density of 19.3 g/cm 3, making it one of the densest metals known.
- Melting point:Gold melts at a relatively low temperature of 1064.4 °C, which is higher than most other metals.
- Electrical conductivity:Gold is an excellent conductor of electricity, with a conductivity of 45.2 MS/m.
- Thermal conductivity:Gold also possesses high thermal conductivity, allowing it to transfer heat efficiently.
- Color:Gold has a distinctive yellow color that is often associated with wealth and luxury.
Extensive Properties
Extensive properties are those that depend on the amount of gold present. They include:
- Mass:The mass of gold refers to the quantity of matter it contains, typically measured in grams or kilograms.
- Volume:The volume of gold represents the amount of space it occupies, typically measured in cubic centimeters or liters.
- Length:The length of gold refers to the distance between two points on a piece of gold, typically measured in millimeters or centimeters.
- Area:The area of gold represents the surface area it covers, typically measured in square millimeters or square centimeters.
Chemical Properties of Gold
Gold is known for its chemical inertness, making it highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion. This property has contributed to its enduring value and use in various applications.
Chemical Inertness
Gold does not react with most chemicals, including oxygen, water, and acids. This inertness makes it an ideal material for jewelry, coins, and other decorative objects that require resistance to tarnishing and degradation.
Alloys
Despite its inertness, gold can form alloys with other metals, such as copper, silver, and platinum. These alloys alter the properties of gold, such as its color, hardness, and melting point. Gold alloys are often used in jewelry, dentistry, and electronics.
Chemical Reactions
Gold does react with a few substances, including aqua regia, a mixture of concentrated nitric and hydrochloric acids. This reaction is used in the refining and purification of gold.
Applications of Gold
Gold has a wide range of applications due to its unique properties. It is commonly used in the following areas:
Jewelry and Coinage
Gold is a popular material for jewelry, coins, and other decorative objects. Its beauty, durability, and high value make it a sought-after choice for personal adornment and investment.
Industrial Applications
Gold is used in various industrial applications, including:
- Electronics:Gold is used in electrical connectors, printed circuit boards, and other electronic components due to its high electrical conductivity.
- Dentistry:Gold is used in dental crowns, bridges, and other dental restorations due to its biocompatibility and durability.
- Medicine:Gold is used in certain medical applications, such as cancer treatment and drug delivery systems.
Investment and Safe Haven
Gold is often considered a safe haven asset during economic uncertainty. Its value tends to hold steady or even increase during periods of market volatility, making it a popular choice for investors seeking to preserve capital.
Occurrence and Extraction of Gold

Gold occurs naturally in the Earth’s crust in various forms, including:
Natural Occurrence
- Ores:Gold is found in ores, which are rocks containing gold-bearing minerals. The most common gold ore is quartz.
- Alluvial Deposits:Gold can also be found in alluvial deposits, which are formed when gold-bearing rocks are eroded and transported by water.
Extraction Methods
Gold is extracted from its ores using various methods, including:
- Cyanidation:This method involves dissolving gold from the ore using a cyanide solution.
- Amalgamation:This method involves mixing the ore with mercury to form an amalgam, which is then separated to recover the gold.
- Gravity Separation:This method utilizes the difference in density between gold and other materials to separate the gold particles.
Environmental Impact
Gold mining can have a significant environmental impact, including water pollution, deforestation, and soil erosion. Sustainable mining practices are essential to minimize these impacts.
FAQs: Classify The Following As Intensive Or Extensive Properties Of Gold
What are intensive properties?
Intensive properties are independent of the amount of substance. They include density, melting point, and boiling point.
What are extensive properties?
Extensive properties depend on the amount of substance. They include mass, volume, and energy.
What are some examples of intensive properties of gold?
Some examples of intensive properties of gold include its density, melting point, and electrical conductivity.
What are some examples of extensive properties of gold?
Some examples of extensive properties of gold include its mass, volume, and heat capacity.