Embark on a comprehensive journey through the foundational principles of macroeconomics with our expert guide to Principles of Macroeconomics Exam 1. Discover the intricacies of macroeconomic variables, national income and output, inflation and unemployment, and delve into the realms of economic growth, fiscal and monetary policies, and international economics.
Prepare to unravel the complexities of macroeconomic phenomena and gain a profound understanding of the forces that shape our economic landscape.
Basic Principles of Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the economy as a whole, including its structure, performance, and policies. It examines the behavior of the economy as a system, focusing on aggregate variables such as output, income, unemployment, inflation, and interest rates.
Macroeconomics differs from microeconomics, which focuses on the behavior of individual entities within the economy, such as consumers, firms, and industries. Macroeconomic variables are typically measured at the national or international level, and macroeconomic policies are designed to influence the economy as a whole.
Examples of Macroeconomic Variables, Principles of macroeconomics exam 1
- Gross domestic product (GDP)
- Unemployment rate
- Inflation rate
- Interest rates
- Exchange rates
National Income and Output
Gross domestic product (GDP) is the total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a given period of time, typically a year. GDP is the most comprehensive measure of a country’s economic activity.
GDP can be calculated using three different methods:
- Value-added method:Sums the value added at each stage of production.
- Income method:Adds up all income earned by factors of production.
- Expenditure method:Calculates total spending on goods and services.
GDP is a useful measure of economic well-being, but it has some limitations. GDP does not measure non-market activities, such as housework or volunteer work, and it can be affected by inflation and changes in the price level.
Inflation and Unemployment
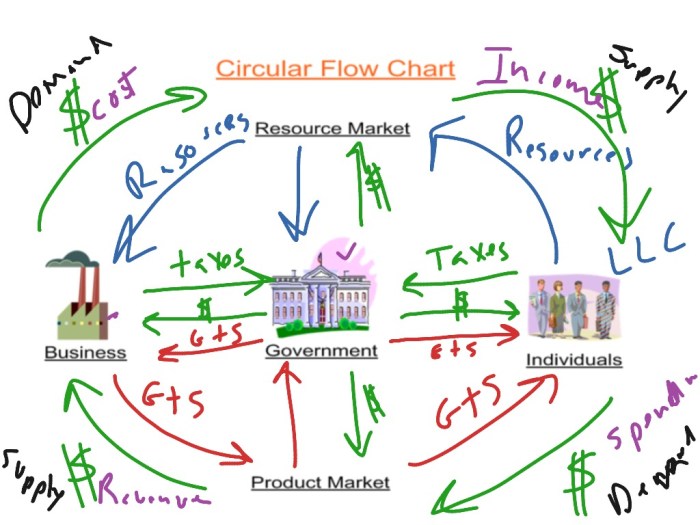
Inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time. Unemployment is a situation where people who are willing and able to work are unable to find a job.
There are different types of inflation, including demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and hyperinflation. Similarly, there are different types of unemployment, including frictional unemployment, structural unemployment, and cyclical unemployment.
Inflation and unemployment are often inversely related. When inflation is high, unemployment tends to be low, and vice versa. This relationship is known as the Phillips curve.
Economic Growth and Development

Economic growth refers to an increase in the productive capacity of an economy over time. Economic development refers to the process of improving the economic well-being of a country or region.
There are many factors that contribute to economic growth, including capital accumulation, technological progress, and human capital. Economic development can be measured using various indicators, such as GDP per capita, literacy rates, and life expectancy.
Economic growth and development bring many benefits, such as increased living standards, improved health outcomes, and reduced poverty. However, they can also lead to challenges, such as environmental degradation and inequality.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy refers to the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy. Expansionary fiscal policy involves increasing government spending or reducing taxes to stimulate economic growth. Contractionary fiscal policy involves decreasing government spending or increasing taxes to slow down economic growth.
Fiscal policy can be used to address a variety of economic issues, such as unemployment, inflation, and economic growth. However, it can also have negative consequences, such as increased government debt and crowding out of private investment.
Monetary Policy: Principles Of Macroeconomics Exam 1
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by a central bank to control the money supply and interest rates in an economy. Expansionary monetary policy involves increasing the money supply or lowering interest rates to stimulate economic growth. Contractionary monetary policy involves decreasing the money supply or raising interest rates to slow down economic growth.
Monetary policy can be used to address a variety of economic issues, such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. However, it can also have negative consequences, such as financial instability and asset bubbles.
International Economics
International economics is the study of economic interactions between countries. It includes topics such as international trade, foreign exchange, and international finance.
There are different theories of international trade, including the classical theory, the neoclassical theory, and the new trade theory. International trade can have both positive and negative effects on the economies of participating countries.
International finance involves the flow of money and capital between countries. It includes topics such as exchange rates, balance of payments, and foreign direct investment.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?
Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual entities, such as households, firms, and consumers, while macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole, including factors like inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
How is GDP calculated?
GDP can be calculated using three main approaches: the expenditure approach, the income approach, and the value-added approach.
What are the different types of inflation?
There are several types of inflation, including demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and hyperinflation.
How do fiscal and monetary policies affect the economy?
Fiscal policy involves government spending and taxation, while monetary policy involves actions taken by the central bank to control the money supply. Both policies can significantly impact economic growth, inflation, and unemployment.